Hypofractionation in hemostatic radiotherapy in advanced vaginal and cervical cancer. Our experience and review of literature
Ryszard Krynicki1, Agnieszka Nalewczyńska1, Bogusław Lindner2, Beata Śpiewankiewicz1
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
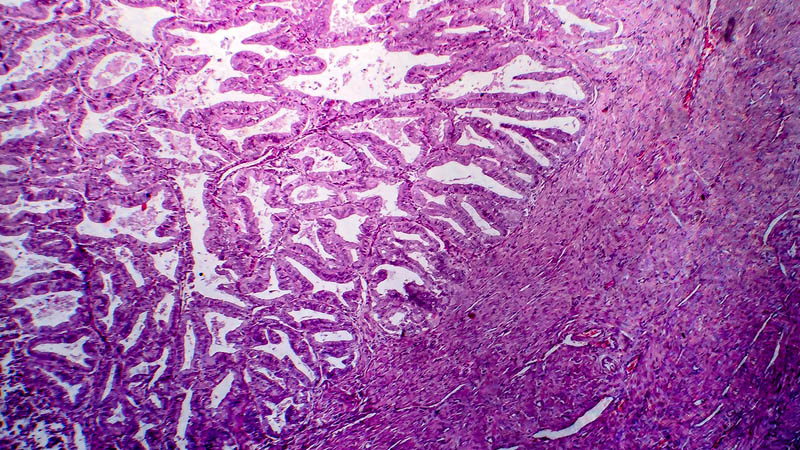
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiIn gynecologic oncology – despite the existence of proven methods of prevention – more than 60% of patients consult the doctor only at the advanced clinical stage of the disease. The first symptom of advanced cervical and vaginal cancer is often heavy bleeding, due to the considerable fragility of the tumor. The aim of the study was to evaluate the impact of dose fractionation method on the effect of palliative hemostatic radiotherapy. In the years 2001–2012, 67 patients with a diagnosis of advanced cervical and vaginal cancer were treated using this method in the Department of Gynecologic Oncology, Marie Skłodowska-Curie Memorial Cancer Center and Institute of Oncology in Warsaw. Because of the massive bleeding, eight patients with cervical cancer required ligation of the illiac vessels by means of laparotomy or laparoscopy. The study group consisted of 63 patients with cervical cancer and four patients with vaginal cancer. A direct hemostatic effect, as measured by complete cessation of vaginal bleeding after radiotherapy, was obtained in 57 (85%) cases. As a result of recurrent bleeding, 16 patients required the second stage of radiotherapy, which was followed by resolution of the above-mentioned symptom. In the analyzed material, no impact of dose fractionation method on the hemostatic effect was observed. A partial response (cessation of bleeding) after the first stage of radiotherapy was mainly achieved in patients with low hemoglobin levels (less than 9 g/dL) and invasive type of tumor growth. In the case of eight patients – due to a marked regression of tumors – it was decided to implement a radical treatment. In all patients, the treatment was well tolerated. None of them had early acute radiation reactions in the bladder or intestines.