Fallopian tube carcinoma – clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment. Case study
Adam Cieminski, Jan Lewandowski, Janusz Emerich
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
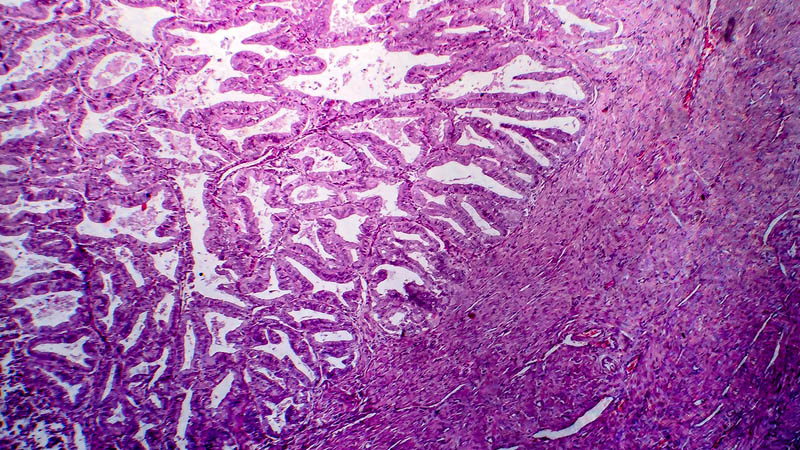
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiPrimary fallopian tube carcinoma (PFTC) is a rare tumor diagnosed mainly between the fourth and sixth decade of the patient’s life. The etiology of this cancer remains unknown. Presumably, genetic, hormonal, and reproductive factors like the ones in ovarian cancer may increase the PFTC risk. The germ-line BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation is the only documented risk factor related to its etiology. Given the rarity of the incidence and diagnostic difficulties concerning the fallopian tube hyperplasic changes in early stages of disease, the diagnosis of PFTC is most often intraoperative and/or happens after the settlement of the final histopathological diagnosis. The pathologic process in early stages is characterized by a stingy or asymptomatic course. The Latzko’s triad, the group of classical symptoms of PFTC, is reported in 15% of cases. It is caused by infilling and decompression of partly blocked oviduct by the pathological process. One of the PFTC signs is the presence of retroperitoneal spread in the endosalpinx before ovaries are involved. The paper presents the case of PFTC treatment in 47-year-old patient diagnosed only intraoperatively, who was subject to conservative treatment 6 months prior to hospitalization – with no result. During this time appropriate diagnosis was not obtained. Combined treatment including surgery and chemotherapy was applied. After obtaining intraoperative positive histopathological exam for fallopian tube neoplastic process, radical surgical treatment was performed. The patient underwent the hysterectomy, adnexectomy, omentectomy, pelvic lymphadenectomy and surgical staging like in ovarian cancer. The adjuvant chemotherapy according to platinum and taxan protocol was administered. The surgical treatment is the base of fallopian tube therapy. In young women in early-stage of the disease, who wish to preserve fertility, conservative treatment is allowed. In other cases hysterectomy, adnexectomy, omentectomy, pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy cytological smears and peritoneum sampling like in ovarian cancer protocol are made. In advanced cases the treatment includes the primary and secondary cytoreduction. In adjuvant therapy the first and the second line chemotherapy is used like in ovarian cancer protocols. At present there are not recommendations for hormonotherapy or adjuvant radiotherapy. The most important prognostic factors are the stage of the disease and the lack of optimal cytoreduction (residual tumor >2 cm). When compared to ovarian cancer, primary fallopian tube cancer more often tends to involve retroperitoneal space and to metastasize distantly. Due to the facts that its clinical symptoms appear earlier, it is diagnosed at earlier stages. A better prognosis regarding the survival in advanced cases points to a different biology of the neoplasm than the one in the ovarian cancer.