Reduction of risk of developing BRCA-dependent cancer in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers – novel approach to old paradigm
Radosław Mądry1, Anna Markowska2
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
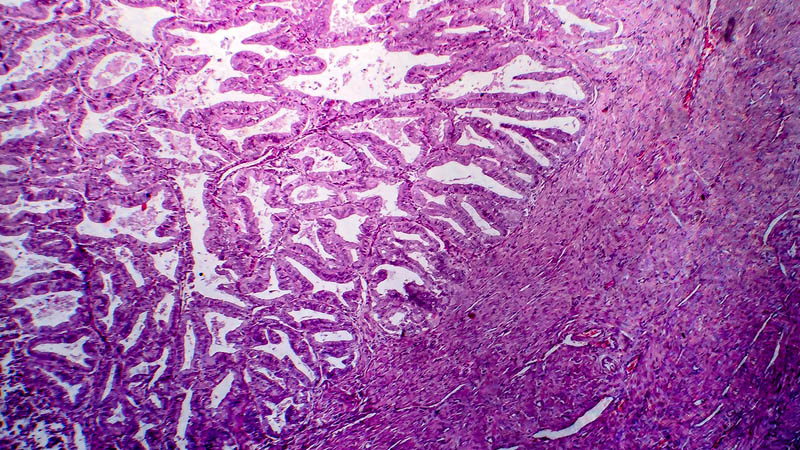
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiCarriers of mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes undergo a significantly increased risk of developing breast cancer, ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer and peritoneal cancer. Due to genetic homogeneity of Polish population, the key issue are mutations of BRCA1 gene. Mutations of 5382insC, C61G and 4153delA constitute about 90% of all BRCA1 gene mutations. Mean cumulative risk of development of ovarian cancer by carriers of BRCA1 gene mutations under 70 is estimated at 40% and that of breast cancer – at 57%. Management of carriers of BRCA1/2 mutations is multidirectional. Carriers of BRCA1 mutations should be screened for breast cancer. Available data indicate that detection of early forms of ovarian cancer is currently impossible. Use of low-dose oral contraception may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer, while not increasing the risk of breast cancer in BRCA1 mutation carriers. After giving birth to planned/desired number of children, carriers of BRCA1 gene mutation should be offered the option of preventive salpingo-oophorectomy. This may reduce the risk of development of BRCA-dependent tumors to 0.21 (95% CI: 0.12-0.39) and breast cancer to 0.49 (95% CI: 0.37-0.65). Risk reduction for the development of peritoneal cancer is not 100% because some of the patients develop primary peritoneal cancer. The risk of development of this type of tumor is significantly reduced to 0.92% vs. 5.78% in the followed-up group. Upon preventive adnexectomy, these patients may safely benefit from hormonal replacement therapy. Close follow-up is mandatory aiming at an early detection of possible metabolic syndromes. Available model analyzing the impact of several strategies of follow-up and intervention on survival rates of mutation carriers indicates that adnexectomy at the age of 40 is the single most effective intervention in BRCA1 mutation carriers.