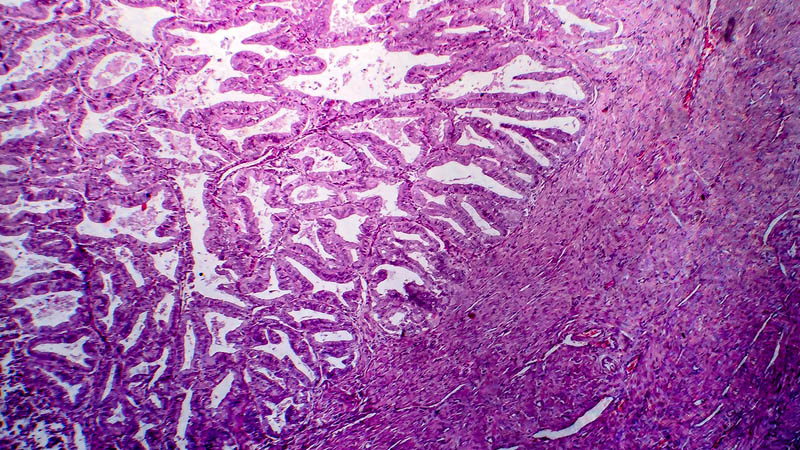
The evaluation of intra- and postoperative complications related to debulking surgery with bowel resection in patients with FIGO stage III-IV ovarian cancer
Mariusz Bidziński, Paweł Derlatka, Izabela Ziółkowska-Seta, Paweł Kubik, Leszek Gmyrek, Piotr Sobiczewski, Anna Dańska-Bidzińska, Grzegorz Panek
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiIntroduction: The surgical treatment of advanced ovarian cancer patients is based on the maximal debulking. In a lot of patients, the necessity of widening operation range to the infiltrated organs takes place. These procedures may be connected with higher risk of intraoperative and early postoperative complications. Sometimes, the exteriorization of ileostomy is necessary, what leads to the quality of life deterioration. Aims of the study: 1) The assessment of the quantity and quality of intra- and postoperative complications in ovarian cancer patients with FIGO stage III-IV in which, to achieve the optimal debulking, partial bowel resection was performed. 2) The evaluation of intra- and postoperative complications, related to surgery with bowel resection, compared to Hartmann surgery in examined group of patients. Material and method: The analysis of 39 debulking surgical procedures with partial intestinal resection and postoperative period in ovarian cancer patients, FIGO stage III-IV, was performed. The following factors were analyzed: the size of excised tumor, the intestinal resection range, method of anastomosis or stoma exteriorization, size of lesions left, blood loss, hemoglobin concentration before and after surgery, quantity and reasons for reoperations, postoperative complications, the length of hospitalizations, time to start with chemotherapy treatment. Results: During 39 operations, the most frequent type of intestinal resection was the sigmoidectomy or proctosigmoidectomy. This kind of surgery was performed in 29 patients. In the remaining patients, left- and right-side hemicolectomy or partial enterectomy was done. There were 24 enteroenterostomies performed, and 15 Hartmann procedures. In 32 patients, the diameter of left tumor lesions was less than 10 mm. Among complications forcing the reoperations were: bleeding in 3 (7.6%) patients, the separation of anastomosis in 3 (7.6%) patients, bowel obstruction in 1 (2.5%) patient, stomach perforation in 1 (2.5%) patient. There were no deaths during postoperative period. There were not noted any differences between surgery with anastomosis and Hartmann surgery in aspect of quantity of complications, blood loss, and the time of surgery. Conclusions: Intestinal resection, during debulking surgery in advanced ovarian cancer patients, brings good results, and complications related to surgery are to be accepted. The quantity of perioperative complications, related to surgery with anastomosis, and to Hartmann surgery is similar. If it is possible, the surgery with enteroenterostomosis should be performed.