Changes in oxygen concentration may involve angiogenesis changing an expression of VEGF receptors – in vitro trophoblast culture study
Grzegorz Szewczyk, Wacław Śmiertka, Jakub Klimkiewicz, Michał Pyzlak, Dariusz Szukiewicz
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
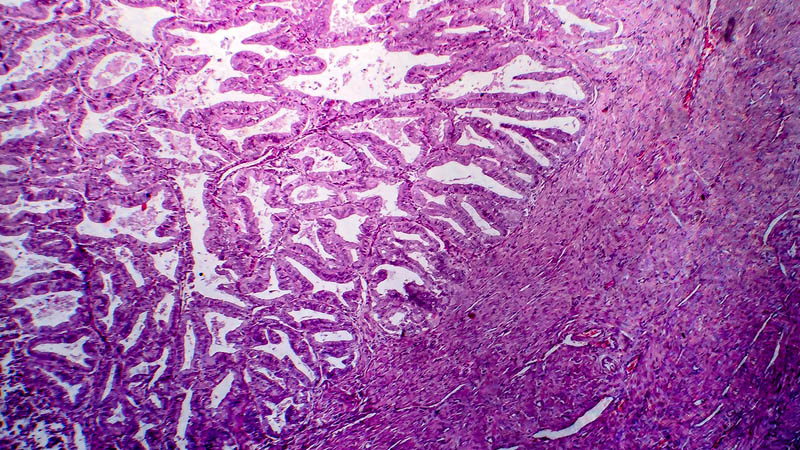
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiAngiogenesis is essential for tissue growth, particularly for the development of fetus and placenta, but also plays a crucial role in pathologic phenomena, e.g. retinopathy or tumors. The key mediator involved in the development of new vessels is vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), acting by specific receptors – VEGF-R1, VEGF-R2 and VEGF-R3. These receptors are present on the surface of cells of developing trophoblast as an expression of auto- and paracrine proangiogenic activity of trophoblast. The aim of this study was to assess the expression of VEGF receptors on cultured trophoblastic cells in vitro, in normoxic or hypoxic conditions. Material and methods: Placentae (n=12) were collected on the occasion of scheduled cesarean sections terminating normal, full-term pregnancies. After excision of tissue fragments, placental tissue was crumbled and trophoblastic cells were isolated by the Kliman technique. Cells were cultured and randomized into two groups. Culture conditions were as follows: group 1: CO2 – 5%; O2 – 20%, N2 – completed; group 2: CO2 – 5%, O2 – 5%, N2 – completed. After 96 hours’ incubation cultures were terminated, supernatant was removed and solid material was fixed in 4% formalin. Immunocytochemical staining for VEGF-R1 and VEGF-R2 was performed. Preparations were evaluated using the morphometric software Quantimet C500+ (Leica). Intensity and surface area of color reaction were analyzed in 20 randomly selected fields of vision (200x). The level of expression of receptors was shown as a product of analyzed parameters and was compared in both groups. Results: The level of expression of VEGF-R1 and VEGF-R2 was greater in the group 2 as compared with the group 1 by 113.9% and 83.6% respectively. Conclusions: Trophoblast culture in hypoxic conditions leads to a greater expression of VEGF receptors than in normoxemic culture.